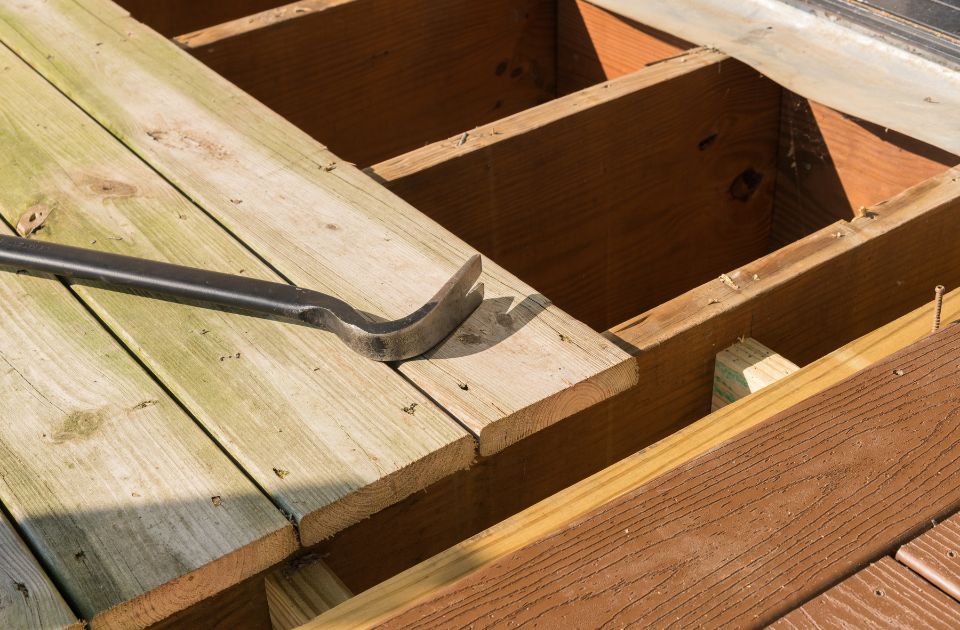
Introduction: What is a floor joist?
A floor joist is a crucial structural component that supports the floor decking and transfers the weight of the floor to the underlying foundation or beams. These beams are typically made of wood, steel, or engineered wood products like laminated veneer lumber. They are strategically placed and spaced to provide stability and prevent sagging or bouncing on the floor.
Floor joists play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and strength of a building’s flooring system. Without them, floors would not be able to support the weight of furniture, occupants, and any additional loads.
To ensure proper installation and longevity, it is important to follow recommended building codes and best practices for sizing, spacing, and attaching floor joists.

The Anatomy of a Floor Frame
A floor frame is a key component of a building structure that provides support and stability to the floor. It consists of several elements, including floor joists, which are horizontal beams that span the width of the floor.
- Floor joists:
These are horizontal beams that run parallel to each other and support the weight of the floor and the load above it. They are typically made of wood or metal and are positioned at regular intervals along the length of the floor frame.
- Subfloor:
The subfloor is a layer of material, such as plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), that is installed on top of the floor joists. It provides a flat and even surface for the finished floor and helps distribute the load across the joists.
- Bridging:
Bridging is a technique used to add additional support and prevent the floor joists from twisting or bending. It involves installing diagonal braces between the joists, which helps distribute the load more evenly and improves the overall structural integrity of the floor frame.
Floor frames also include other components, such as rim and floor joists support there, which are vertical beams that run along the edges of the floor and provide support for the joists. Additionally, floor frames may incorporate other structural elements like beams and columns to further enhance stability and load-bearing capacity.
Understanding the anatomy of a floor frame is crucial for architects, engineers, and construction professionals to ensure the structural integrity and safety of a building. By considering the design, materials, and techniques involved, the construction of a solid floor frame can be achieved.
Don’t miss out on the importance of a well-constructed floor frame. It plays a vital role in providing stability and support to the entire structure of a building.
Whether you are designing or renovating a residential or commercial space, ensure that your floor frame is built to the highest standards to avoid future complications and ensure the long-term durability of the whole floor structure.
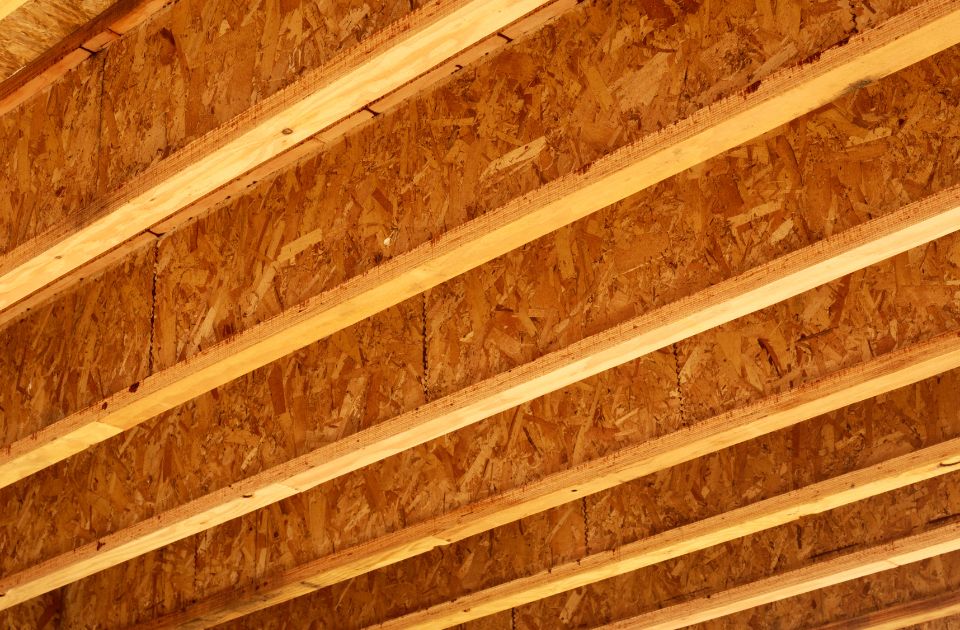

Types of Floor Joist
A full floor joist system is a crucial component of a building’s structure. It provides support and stability to the flooring system. Understanding the various types of floor joists is essential for construction professionals in order to choose the most suitable option for a specific project.
TJI Joists:
These floor joists are engineered wood products that provide strong and reliable support. They are lightweight, versatile, and offer longer spans compared to traditional solid wood joists.
I-Joists:
These joists consist of a vertical web and two horizontal flanges. They are known for their strength and stability, making them ideal for heavy load-bearing applications. I-joists also allow for easy installation of utilities such as wiring and plumbing.
Open Web Joists:
Also referred to as trusses, these joists are made up of a combination of wood and steel components. They are designed to provide efficient support over long spans and are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings.
When selecting a floor joist, factors such as load requirements, span lengths, and cost considerations should be taken into account. It is essential to consult with a structural engineer or a building professional to determine the most suitable type of floor joist for a specific project.
Floor joists have been an integral part of building construction for centuries. They have evolved over time, with advancements in material technology and engineering techniques.
The use of engineered wood products and the introduction of innovative designs have improved the strength and durability of floor joists, ensuring the stability of modern buildings.
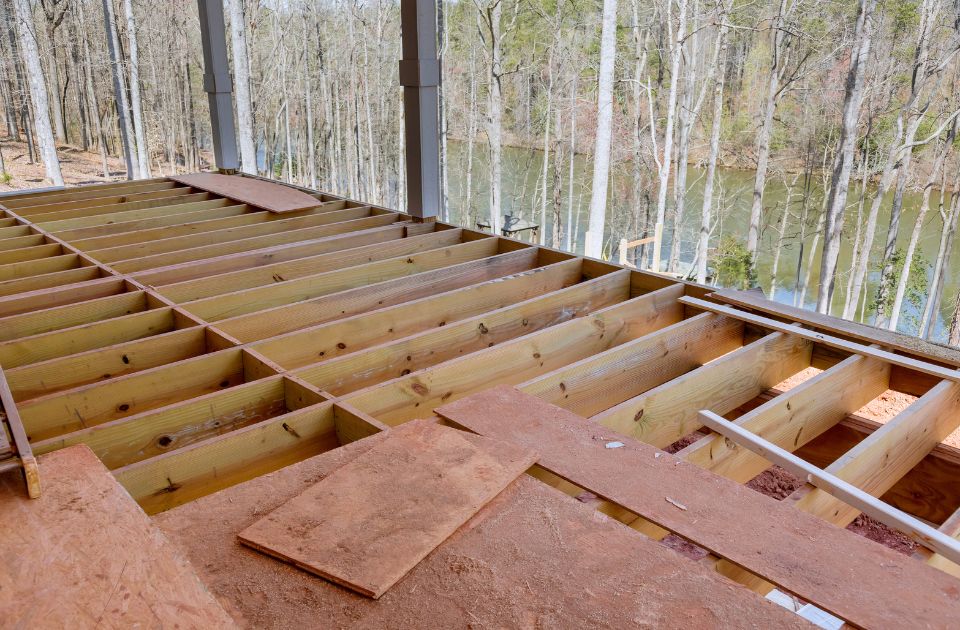

Floor Joist Span Considerations
Joist Span Considerations:
The additional factors that need to be considered when determining the span of floor joists for a project are as follows:
- Load Capacity:
The weight-bearing capacity of the joists is crucial in ensuring a structurally sound floor. Factors such as the intended use of the space and the expected load should be taken into account.
- Joist Material:
The type of material used for the joists will affect their span capabilities. Different materials have varying strength and flexibility, which can impact the maximum distance between supports.
- Joist Size:
The dimensions of the joists, including the width and depth, should be chosen carefully to support the expected load. Thicker and wider joists typically have higher load capacities and can span larger distances.
- Spacing between Joists:
The spacing between joists determines the level of support provided to the flooring above. Closer spacing can distribute the load more evenly and reduce deflection, but it also requires more joists overall.
- Building Codes and Regulations:
Local building codes and regulations often dictate the maximum allowable span for floor joists. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance and safety.
- Additional Support: In some cases, additional support, such as midspan beams or columns, may be necessary to reinforce the joists and prevent sagging or excessive deflection.
Considering these factors will help determine the appropriate span for floor joists, ensuring a robust and durable flooring system.

Wood Species
Types of Wood Species:
Different types of wood are used for floor joists, each with its own unique characteristics and strengths. Here are some common wood species used for floor joists:
SpeciesStrengthDurabilityCostDouglas FirHighHighModerateSouthern PineHighModerateLowSpruce-Pine-FirModerateModerateLow
These are just a few examples of wood species used for floor joists. Each species has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the right wood for your specific needs.
It’s interesting to note that the strength and durability of wood can vary depending on factors such as the growth conditions, age, and treatment of the wood.
Therefore, it’s always advisable to consult with a professional or refer to reliable sources when selecting the wood species for your floor joists. (Source: What Is a Floor Joist, Reference Data)
Grade
In the construction industry, the quality and strength of a floor joist is determined by its grade. The grade of a joist indicates its performance capabilities and load-bearing capacity. Different grades are assigned based on the type and quality of the lumber used in the joist’s construction.
Below is a table outlining the different grades of floor joists and their corresponding characteristics:
Grade Strength (lbs)Highest quality: 1,000+, High quality: 800-1,000, Medium quality: 600-800, Low quality: Less than 600
It is important to choose the appropriate grade of floor joist based on the intended use and load requirements. Each grade has its own set of specifications and limitations, ensuring that the most floor joists used can withstand the expected loads without compromising the structural integrity of the building.
Understanding the grade of a floor joist is essential for architects, engineers, and contractors to make informed decisions during the design and construction process. By selecting the correct grade, the longevity and safety of the structure can be ensured.

Lumber Width
Lumber width refers to the measurement of the width of a piece of lumber. It plays a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of a floor joist. Here is a table showcasing the different lumber width options available:
Width (inches) 2×4 Commonly used for light-duty construction and framing projects. 2×6 Provides more strength and stability than a 2×4 and is often used for heavier loads. 2×8 offers even greater strength and is suitable for larger spans and heavier loads.
2×10 Provides additional strength and is commonly used for longer spans and greater loads. 2×12 offers the highest level of strength and is used for the most demanding structural applications.
It’s important to select the appropriate lumber width based on the specific requirements of your project. Using lumber that is too narrow can compromise the structural integrity of the floor joist, while using lumber that is too wide may be unnecessary and wasteful.
Understanding the load-bearing capacity and span requirements is essential for making the right choice. Consider consulting a professional or referring to local building codes for guidance.
Ensuring the correct lumber width is crucial for the safety and longevity of your floor joists. Don’t miss out on this important detail, as it can impact the overall structural integrity of your construction project. Choose wisely and prioritize the strength and stability of your floor joists to avoid future issues and ensure a solid foundation.

Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight that a floor joist can bear without compromising its integrity. Understanding the load capacity of floor joists is crucial for ensuring the structural stability of a building.
In order to understand the load capacity of floor joists, it is helpful to consider the following information:
Load Capacity Table:
Joist Material Maximum Span (in feet) Maximum Allowable Load (in pounds per square foot)Wood 840 Steel 1260 Concrete 1580
It is important to note that these load capacity values are approximate and may vary depending on factors such as the specific construction materials, spacing of the joists, and the load-bearing capacity of the supporting structures.
In addition to the load capacity of the floor joists themselves, it is also crucial to consider the dead load and live load that will be placed on the floor.
The dead load refers to the weight of the permanent structural elements, such as the floor itself, walls, and fixtures. The live load refers to the weight of the people, furniture, and any movable objects on the floor.
Furthermore, it is important to consult local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance with the recommended load capacity guidelines. Building inspectors and structural engineers can offer valuable insights and guidance regarding load capacity requirements for specific construction projects.
It’s important to note that load capacity can vary depending on the specific type of floor joist used and the construction materials involved. Therefore, it is always best to consult with a professional and refer to reliable sources for accurate load capacity information.
True fact: According to the article “What is a floor joist,” load capacity is a crucial consideration in the design and construction of floor systems to ensure structural integrity.
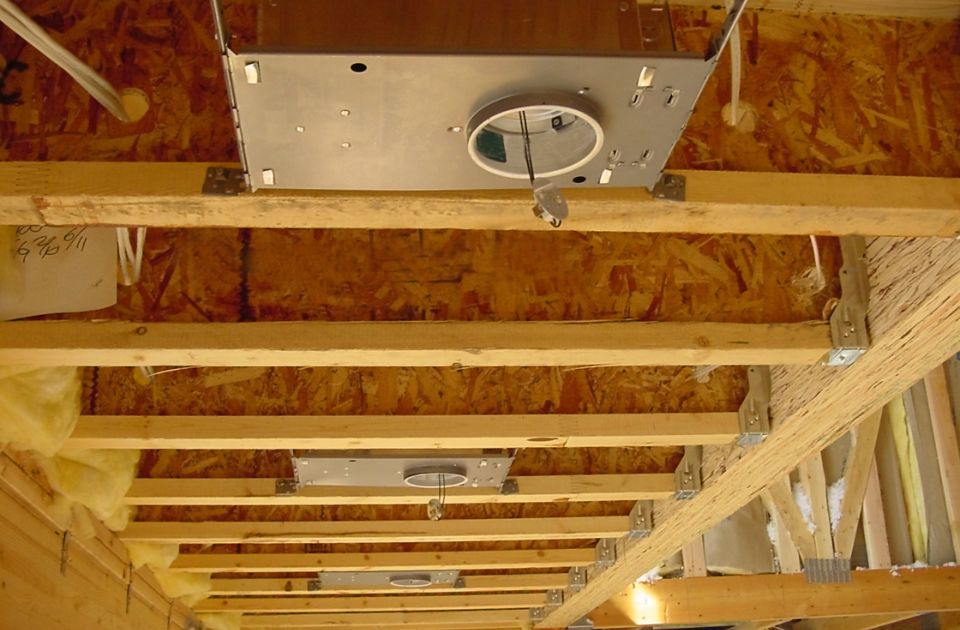

Importance of Understanding Floor Joists
Understanding the Significance of a Floor Joist:
Floor joists play a critical role in the stability and integrity of a building’s structure. An understanding of their importance is crucial for any construction project.
These horizontal beams provide support for the floor and distribute the weight evenly, ensuring that the structure can withstand various loads and forces.
By comprehending the significance of floor joists, builders can create safe and durable buildings that meet the necessary structural requirements.
In considering the importance of understanding floor joists, it is vital to recognize their role in preventing sagging or unevenness in floors. Their correct installation and spacing prevent the floor from sagging over time, providing stability and comfort for occupants.
Furthermore, floor joists also allow for the proper distribution of loads, such as furniture, appliances, or heavy equipment, ensuring that the same standard floor joist can support these additional weights without compromising its structural integrity. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of floor joists is essential for architects, engineers, contractors, and anyone involved in the construction industry.
Covering a unique detail, it is worth noting that floor joists can be made from various materials, including wood, steel, or engineered wood products. Each material has its advantages and considerations, such as cost, strength, and sustainability.
Understanding these material options allows builders to make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of a project, ensuring the best possible outcome in terms of efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
To illustrate the significance of understanding floor joists, consider the case of a residential building that neglected to install proper floor joists during construction. Over time, the occupants noticed significant sagging and unevenness in the floors, causing discomfort and safety concerns.
Eventually, the floors became so unstable that they required extensive repairs and reinforcement, leading to significant financial and time burdens. This story emphasizes the crucial role of floor joists and the consequences of overlooking their importance.
By viewing floor joists as a fundamental element of construction, professionals can comprehend their significance beyond mere beams. Understanding their crucial role in providing stability, preventing sagging, and accommodating additional loads is vital for ensuring safe and durable structures.
Whether it be choosing the appropriate materials or installing them correctly, the importance of understanding floor joists cannot be overstated in the construction industry.

Five Facts About Floor Joists:
✅ Floor joists are horizontal structural members that span an open space and transfer the load to vertical structural members. (Source: Team Research)
✅ Floor joists help distribute the weight of everything inside a room, including walls, furniture, appliances, and people. (Source: Team Research)
✅ Most often, floor joist spacing is 16 inches apart on center, but this can vary depending on building codes and structural requirements. (Source: Team Research)
✅ There are different types of floor joists, including solid lumber joists, I-joists (TJI joists), and open-web floor trusses. (Source: Team Research)
✅ Factors to consider when selecting floor joists include wood species, grade, lumber width, and load capacity. (Source: Team Research)

FAQs about What Is A Floor Joist
What is a floor joist, and what is its purpose?
A floor joist is a horizontal structural member that spans an open space and transfers the load to vertical structural members. It is part of the floor system and supports the weight of everything inside a room, including walls, furniture, appliances, and people.
How far apart should floor joists be spaced?
Floor joist spacing is typically 16 inches apart on center, but this can vary depending on building codes and the requirements of the structure in the blueprint. The same standard floor joist spacing is important to evenly distribute the load and ensure the structural integrity of the floor.
What are the different types of floor joists?
The three common types of floor joists are solid lumber joists, I-joists (TJI joists), and open-web floor trusses. Solid lumber floor joists run perpendicular and are contiguous boards, I-joists have a capital I shape and are made with different materials, and open-web floor trusses use wood pieces cantilevered to support floor loads.
What are the pros and cons of solid lumber joists?
Pros of solid lumber joists include longer fire resistance and lower cost compared to engineered solutions. Cons include environmental concerns due to the depletion of older trees and limited span distances.
What are the pros and cons of I-joists?
Pros of I-joists include longer spans and lighter weight for easier maneuvering during construction. Cons include faster failure in fires and higher costs compared to solid lumber joists.
What are the factors to consider when determining joist size and span?
Factors to consider include the type of floor joist, the dimensional lumber used, building codes, wood species, lumber grade, lumber width, and load capacity. These factors influence the structural strength and span distance of the floor joists.

Key Takeaways:
A floor joist is a horizontal structural member that supports the weight of a floor and transfers it to the foundation or load-bearing walls. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and stability of a building’s floor system.
The anatomy of a floor frame consists of various components, and a floor joist is one of them. It is typically made of wood or steel and runs parallel to each other to create a framework that supports the floor and distributes weight evenly.
There are different types of floor joists available, including dimensional lumber joists, engineered wood joists, and steel joists. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, such as cost, span capabilities, and load-bearing capacity.
When determining the joist span, several factors need to be considered, such as the length of the span, the type of joist used, and the intended load. It is crucial to follow building codes and guidelines to ensure the proper spacing and support for the floor joists.
The choice of wood species for floor joists is essential as different species have different strength and stability properties. Commonly used wood species include Douglas fir, Southern pine, and Spruce-Pine-Fir (SPF).
The grade of lumber used for floor joists determines the quality and strength of the material. Higher-grade lumber typically has fewer defects and is more suitable for structural applications.
The width of the lumber used for floor joists affects the load capacity and stability. Wider joists generally provide better load-carrying capabilities and can span longer distances without additional support.
The load capacity of floor joists depends on various factors, including the type of joist, the span, and the intended use. It is crucial to ensure that the floor joists can support the weight of the floor, furniture, occupants, and any additional loads.
Understanding floor joists is important for architects, builders, and homeowners alike, as it helps ensure the safety, durability, and performance of a building’s floor system. Properly designed and installed floor joists contribute to the overall structural integrity and longevity of a building.